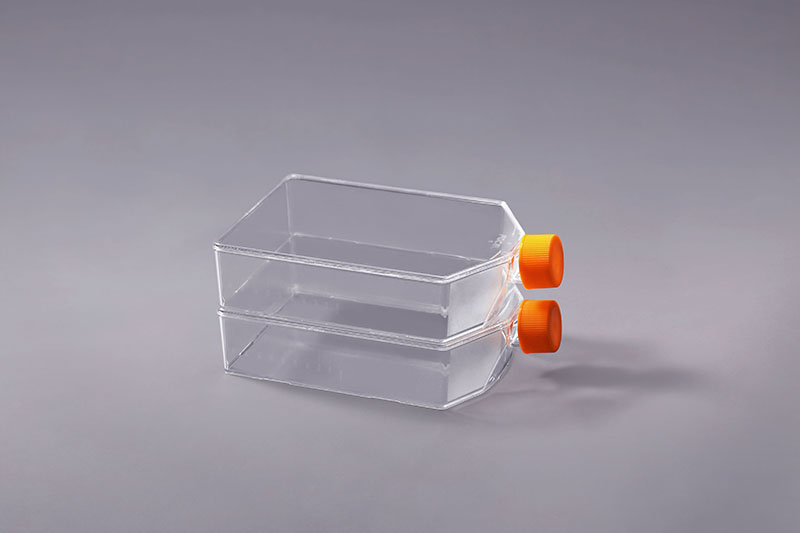
Cell culture flasks are a type of consumables commonly used in the cell culture process. Cell growth has higher requirements for the environment, and the selection of consumables must also meet the requirements of pyrogen-free. Then, what does pyrogen-free mean?
There are two types of pyrogens. One is the endogenous pyrogen, which acts on the body temperature regulation center of the hypothalamus and is a protein that can raise body temperature. One is exogenous pyrogen, which refers to foreign substances that can be the cause of fever. It usually works by inducing endogenous pyrogens. What we usually call pyrogen-free consumables such as cell culture flasks refers to exogenous pyrogens.
Exogenous pyrogens are mainly bacterial pyrogens, which are metabolites of certain bacteria, bacterial corpses and endotoxins. Gram-negative bacilli have the strongest heat-causing ability, followed by gram-positive bacilli. Gram-positive cocci are weaker. Molds, yeasts, and even viruses can also produce pyrogens. The pyrogen is usually a complex formed by the combination of phospholipid polyol and protein. Phospholipid polyol is the active center of the complex and has the strongest pyrogenic effect. Its chemical composition varies with different strains. The molecular weight is 5×104 to 5×105, and the closer the molecular weight, the stronger the thermal effect. In the cell culture process, if the consumables contain pyrogens, it will directly affect the growth and reproduction of the cells, so these consumables must undergo special treatment to remove possible exogenous endotoxins and ensure the normal growth of cells.
In addition to cell culture flasks, consumables such as micropipettes and matching tips used in cell culture need special treatment to eliminate pyrogens before they can be put into use.
The FAI climbed 5.9 percent year-on-year in the first 11 months of 2018, quickening from the 5.7-percent growth in Jan-Oct, the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) said Friday in an online statement.
The key indicator of investment, dubbed a major growth driver, hit the bottom in August and has since started to rebound steadily.
In the face of emerging economic challenges home and abroad, China has stepped up efforts to stabilize investment, in particular rolling out measures to motivate private investors and channel funds into infrastructure.
Friday's data showed private investment, accounting for more than 60 percent of the total FAI, expanded by a brisk 8.7 percent.
NBS spokesperson Mao Shengyong said funds into weak economic links registered rapid increases as investment in environmental protection and agriculture jumped 42 percent and 12.5 percent respectively, much faster than the average.
In breakdown, investment in high-tech and equipment manufacturing remained vigorous with 16.1-percent and 11.6-percent increases respectively in the first 11 months. Infrastructure investment gained 3.7 percent, staying flat. Investment in property development rose 9.7 percent, also unchanged.
 English
English