Cell factory systems are an ingeniously designed device for large-scale cell culture, mainly used in large-scale cell culture, such as the production of vaccines, monoclonal antibodies and the pharmaceutical industry.
In the vaccine industry, cell factory systems have been widely used to produce a variety of vaccines, such as Japanese encephalitis vaccines. The impact of cell factory on the vaccine industry is mainly reflected in the following aspects:
Improve production efficiency: The cell factory has the advantages of large culture area and small space occupation. It can provide the largest culture area in a limited space, thus improving the production efficiency of vaccines. For example, when producing hepatitis A vaccines, cell culture and virus amplification technologies in cell factories are already very mature and can greatly improve vaccine production efficiency.
Reduce production costs: The use of cell factories can reduce enterprises’ quality control costs and downstream purification costs. In addition, since the risk of contamination in cell factories is lower, losses in vaccine production can be reduced, thus reducing production costs.
Promote the automation of vaccine production: With the development of technology, cell factories are gradually replaced by automated production. Automated production can reduce errors caused by manual operations and improve the controllability and stability of the production process, thus improving the quality and reliability of vaccines.
Promote the integration of vaccine R&D and production: The use of cell factories can make vaccine R&D and production more closely integrated. During the vaccine development stage, cell factories can be used for vaccine production and testing to better understand the production characteristics and quality control requirements of the vaccine. This will also help speed up the development and launch of vaccines.
In summary, the use of cell factories can improve vaccine production efficiency, reduce production costs, promote vaccine production automation, and promote the integration of vaccine R&D and production. These effects are important for improving the quality and reliability of vaccines, reducing the price of vaccines, and promoting vaccine production.
The FAI climbed 5.9 percent year-on-year in the first 11 months of 2018, quickening from the 5.7-percent growth in Jan-Oct, the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) said Friday in an online statement.
The key indicator of investment, dubbed a major growth driver, hit the bottom in August and has since started to rebound steadily.
In the face of emerging economic challenges home and abroad, China has stepped up efforts to stabilize investment, in particular rolling out measures to motivate private investors and channel funds into infrastructure.
Friday's data showed private investment, accounting for more than 60 percent of the total FAI, expanded by a brisk 8.7 percent.
NBS spokesperson Mao Shengyong said funds into weak economic links registered rapid increases as investment in environmental protection and agriculture jumped 42 percent and 12.5 percent respectively, much faster than the average.
In breakdown, investment in high-tech and equipment manufacturing remained vigorous with 16.1-percent and 11.6-percent increases respectively in the first 11 months. Infrastructure investment gained 3.7 percent, staying flat. Investment in property development rose 9.7 percent, also unchanged.
 English
English

















































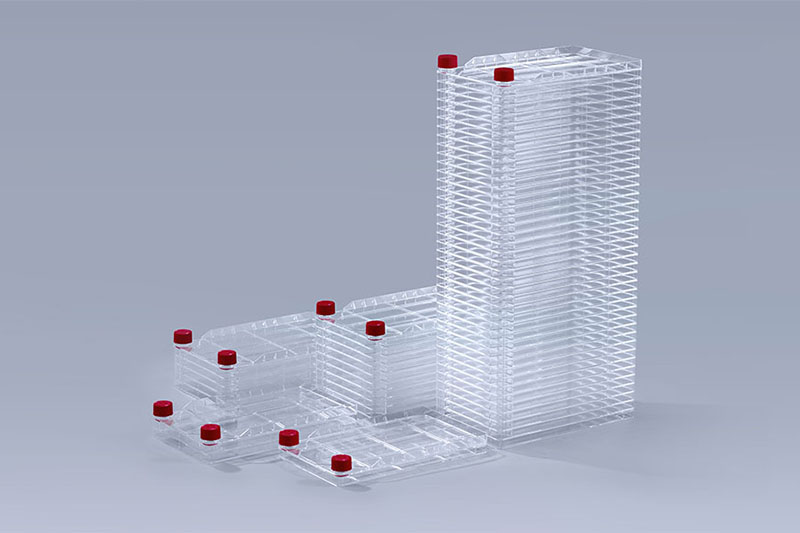 Cell Factory Systems
Cell Factory Systems