In the field of life sciences, cell culture flasks are crucial consumables that directly impact experimental results and production efficiency. Whether in scientific research or industrial production, the quality of cell culture flasks determines the growth and proliferation of cells. Therefore, understanding and choosing high-quality products is essential for ensuring experimental success and production efficiency. This article will introduce the four major factors to focus on when selecting cell culture flasks, helping you make informed decisions.
Product Material: Choosing Between Plastic and Glass
Cell culture flasks primarily come in two materials: plastic and glass.
Plastic Material: Typically used as disposable containers. Plastic cell culture flasks undergo strict quality control during production. Their advantages include ease of use, low cost, and eliminating the hassle of cleaning and sterilizing, making them increasingly popular in the market. Plastic flasks have good chemical resistance and breakage resistance, making them suitable for large-scale production and routine experiments.
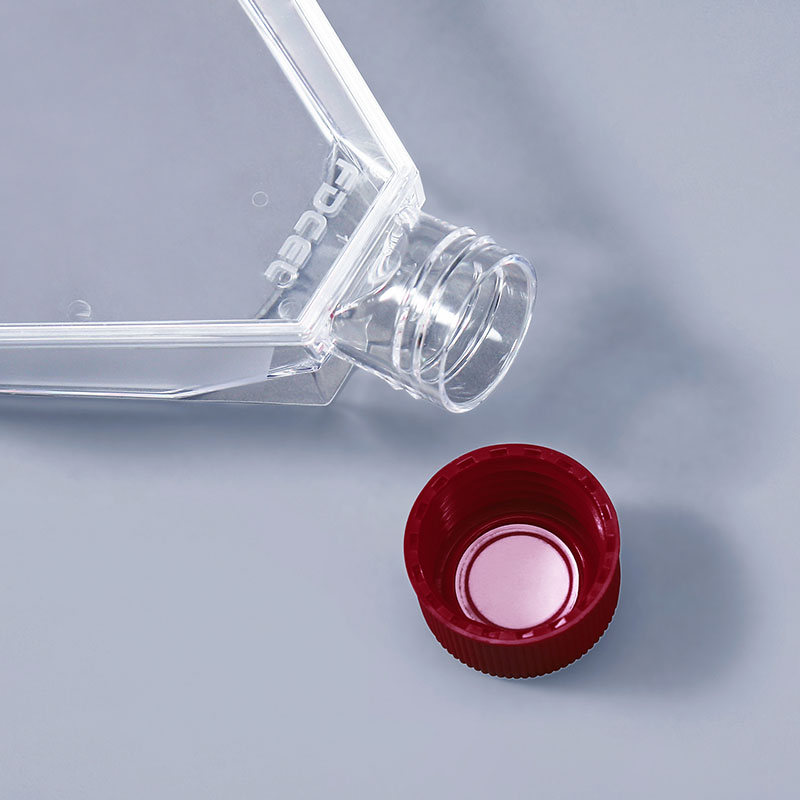

Glass Material: Reusable, but requiring cleaning, drying, and sterilization. While glass flasks have the advantage of being reusable, their fragility and high cleaning and sterilization costs have led to their gradual replacement by plastic in modern cell culture. Glass flasks may also have unpredictable effects on cell growth, so their maintenance cost and potential impact on experimental results need to be carefully considered when choosing.
Processing Technology: The Necessity of Surface Treatment
Suspension Cell Culture: For the culture of suspension cells, the surface treatment requirements for the inner surface of the cell culture flask are relatively low. The focus is on the overall quality and sterility of the container.
Adherent Cell Culture: For the culture of adherent cells, the inner surface of the flask requires special treatment to promote cell attachment and growth. These treatments include surface coatings (such as collagen, fibronectin, etc.) and methods like plasma treatment, which help improve cell adhesion and growth efficiency, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of experiments.
Sterility: Production Environment and Sterilization Method
The sterility of cell culture flasks is critical, as any microbial contamination can affect the results of cell culture. The following are key points to ensure sterility:
Production Environment: High-quality cell culture flasks should be produced in Class C cleanrooms to reduce contamination risks. A cleanroom with strict environmental control can effectively reduce airborne microorganisms and dust, ensuring the sterility of the product.
Sterilization Method: After production, cell culture flasks generally undergo irradiation sterilization, which effectively kills bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms, ensuring the product remains sterile, endotoxin-free, and non-cytotoxic. Choosing cell culture flasks that have undergone reliable sterilization treatments significantly reduces the risk of experimental failure.
Choosing high-quality cell culture flasks is one of the key factors for ensuring the success of cell culture experiments. By focusing on product material, processing technology, and sterility, you can select the right cell culture flasks for your needs, ensuring optimal cell growth and proliferation. Whether in scientific research or industrial production, high-quality cell culture flasks will provide reliable support, improving the accuracy of experiments and the efficiency of production.
The FAI climbed 5.9 percent year-on-year in the first 11 months of 2018, quickening from the 5.7-percent growth in Jan-Oct, the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) said Friday in an online statement.
The key indicator of investment, dubbed a major growth driver, hit the bottom in August and has since started to rebound steadily.
In the face of emerging economic challenges home and abroad, China has stepped up efforts to stabilize investment, in particular rolling out measures to motivate private investors and channel funds into infrastructure.
Friday's data showed private investment, accounting for more than 60 percent of the total FAI, expanded by a brisk 8.7 percent.
NBS spokesperson Mao Shengyong said funds into weak economic links registered rapid increases as investment in environmental protection and agriculture jumped 42 percent and 12.5 percent respectively, much faster than the average.
In breakdown, investment in high-tech and equipment manufacturing remained vigorous with 16.1-percent and 11.6-percent increases respectively in the first 11 months. Infrastructure investment gained 3.7 percent, staying flat. Investment in property development rose 9.7 percent, also unchanged.
 English
English