Cell factories which are multi-layered cell culture containers, are widely used in various applications in the life sciences field. Their versatility and scalable design make them ideal for a range of purposes, including the following:
Cell Cultivation and Expansion
Cell factories are extensively used for cell cultivation and expansion in laboratory research. The number of layers in the cell factory can be adjusted to provide varying scales of culture space, making them adaptable for both small-scale laboratory studies and large-scale cell production. This flexibility allows for efficient scaling in different research and industrial contexts.
Drug Screening and Development
During drug development, cell factories play a crucial role in drug screening and evaluation. By cultivating cells in a multi-layered cell factory, researchers can simulate in vivo environments to assess the effects and toxicity of potential drugs, thus accelerating the development process for new pharmaceuticals.
Biotechnology and Bioproduction
In the fields of biotechnology and bioengineering, cell factories are integral for large-scale production of recombinant proteins, antibodies, vaccines, and other bioproducts. The multi-layer structure of these cell factories allows for more efficient use of space and resources, thus enhancing production efficiency and lowering costs.
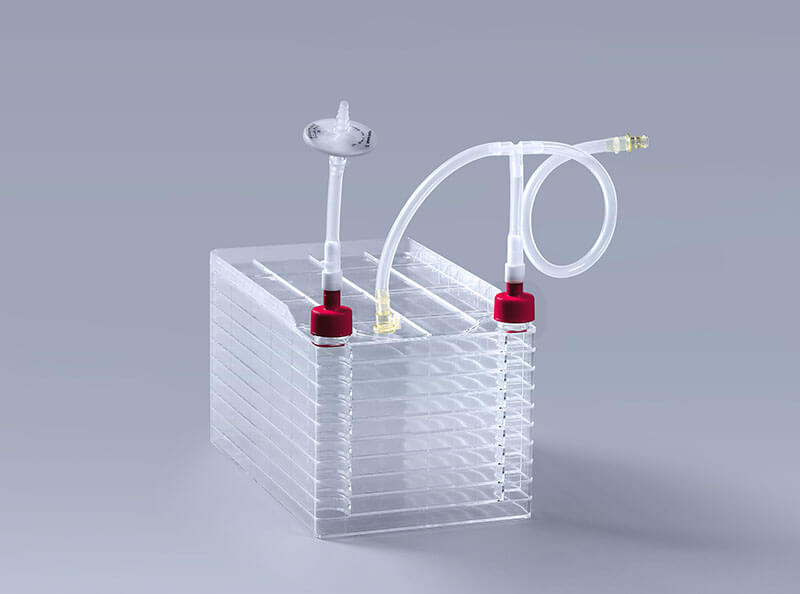
Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine
In tissue engineering and regenerative medicine research, cell factories are used to culture and expand stem cells, fibroblasts, and other cell types for the preparation of tissue scaffolds or for direct transplant applications, such as the regeneration of skin, cartilage, and other tissues. Their ability to provide a controlled environment for cell growth is critical in the development of regenerative therapies.
Gene Editing and Gene Expression Studies
In gene editing research, including CRISPR/Cas9 technologies, cell factories offer a platform for large-scale culturing of genetically modified cells. They are also essential for studies on gene expression regulation, signal transduction pathways, and related areas, providing a robust environment for these complex biological processes.
In summary, the multi-layered structure and adaptable nature of cell factories make them indispensable tools in life science research. They are widely used in cell culture, drug development, bioproduction, tissue engineering, and gene research, playing a critical role in advancing scientific discoveries and industrial applications.
The FAI climbed 5.9 percent year-on-year in the first 11 months of 2018, quickening from the 5.7-percent growth in Jan-Oct, the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) said Friday in an online statement.
The key indicator of investment, dubbed a major growth driver, hit the bottom in August and has since started to rebound steadily.
In the face of emerging economic challenges home and abroad, China has stepped up efforts to stabilize investment, in particular rolling out measures to motivate private investors and channel funds into infrastructure.
Friday's data showed private investment, accounting for more than 60 percent of the total FAI, expanded by a brisk 8.7 percent.
NBS spokesperson Mao Shengyong said funds into weak economic links registered rapid increases as investment in environmental protection and agriculture jumped 42 percent and 12.5 percent respectively, much faster than the average.
In breakdown, investment in high-tech and equipment manufacturing remained vigorous with 16.1-percent and 11.6-percent increases respectively in the first 11 months. Infrastructure investment gained 3.7 percent, staying flat. Investment in property development rose 9.7 percent, also unchanged.
 English
English