Cell factories, which are used for large-scale production of cells or cellular products, must adhere to strict quality standards to ensure the safety, efficacy, and consistency of the final products. These standards are critical in various fields, including biopharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and regenerative medicine. Here are some of the key quality standards and guidelines that cell factories should follow:
1.Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP):
GMP is a set of regulations and guidelines that ensure the consistent quality and safety of pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical products.
Cell factories involved in producing therapeutic cells or cellular products for human use must adhere to GMP standards, including cleanroom requirements, documentation, and quality control procedures.
2.ISO Standards:
International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has several standards relevant to cell factory operations, such as ISO 9001 (Quality Management System) and ISO 13485 (Quality Management System for Medical Devices).
ISO standards provide a framework for quality management, documentation, and process control.
3.Cell Therapy Specific Guidelines:
Depending on the nature of the cell product, cell factories may need to adhere to specific guidelines or regulations. For example:
In the United States, the FDA provides guidelines for the development and manufacture of cellular therapies.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has similar guidelines for cell-based medicinal products.
The International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) may also provide relevant guidelines.
4.Biological Safety:
Cell factories should implement measures to prevent contamination, maintain biological safety, and minimize the risk of adventitious agents.
This includes proper facility design, sterilization, and monitoring for microbial and viral contaminants.
Adhering to these quality standards is essential for the successful and ethical operation of cell factories, especially when producing cellular therapies or products for clinical use. Compliance with these standards helps ensure the safety, efficacy, and consistency of cell-based products and fosters trust among regulators, healthcare providers, and patients.
The FAI climbed 5.9 percent year-on-year in the first 11 months of 2018, quickening from the 5.7-percent growth in Jan-Oct, the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) said Friday in an online statement.
The key indicator of investment, dubbed a major growth driver, hit the bottom in August and has since started to rebound steadily.
In the face of emerging economic challenges home and abroad, China has stepped up efforts to stabilize investment, in particular rolling out measures to motivate private investors and channel funds into infrastructure.
Friday's data showed private investment, accounting for more than 60 percent of the total FAI, expanded by a brisk 8.7 percent.
NBS spokesperson Mao Shengyong said funds into weak economic links registered rapid increases as investment in environmental protection and agriculture jumped 42 percent and 12.5 percent respectively, much faster than the average.
In breakdown, investment in high-tech and equipment manufacturing remained vigorous with 16.1-percent and 11.6-percent increases respectively in the first 11 months. Infrastructure investment gained 3.7 percent, staying flat. Investment in property development rose 9.7 percent, also unchanged.
 English
English

















































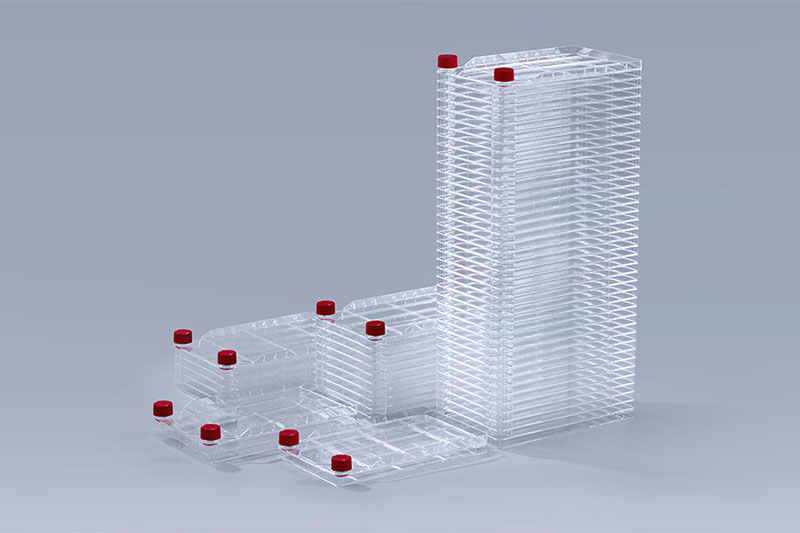 Cell Factory
Cell Factory