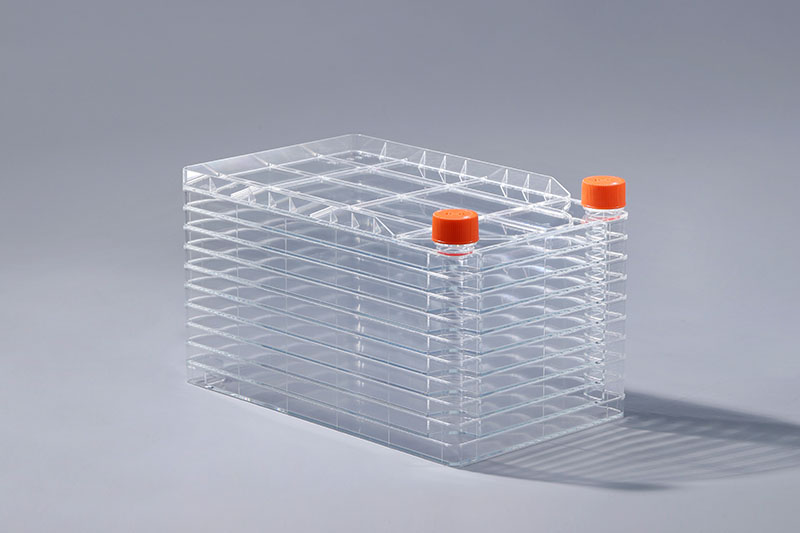
Mold contamination is one of the things that researchers are very worried about in cell culture experiments, often leading to project delays and the loss of scarce cells. So how should mold contamination in cell factories be dealt with to reduce losses?
Judgment of contamination: There are many types of fungi, most of which contaminate cells are Aspergillus, Candida albicans, yeast, black mold, spore fungi, etc. After mold contamination, light yellow or white floating objects are often formed in the culture medium, which are visible to the naked eye and can be easily detected. The culture medium generally remains cloudy in a short period of time. Under an inverted microscope, filamentous, dendritic or tubular hyphae that crisscross the cells can be seen, floating in the culture medium. Many hyphae can be seen in a chain-like arrangement of strains under high magnification. Candida and yeast strains are oval in shape and grow scattered on and around cells. Sometimes hyphae growing on the outer wall of the culture flask may be found by microscope, which is easy to be mistaken for contamination. When the mycelium outside the bottle is found, it should be wiped clean with alcohol in time.
Treatment of contamination: First, it is necessary to determine whether the contaminants in the cell factory are mold contamination. If it is confirmed that it is mold contamination, the contaminated cells should be isolated from other cell lines as soon as possible, and the equipment and reagents used in the experiment should be treated at the same time. In general, high concentrations of both antibiotics and antimycins may have toxic effects on cells or cell lines. Therefore, dose-response experiments are used to determine the dose levels at which antibiotics and antimycins produce toxicity. This is especially important when taking antimycotics such as tylosin.
In summary, the treatment of mold contamination in cell factories can be carried out according to the above methods. In addition, in cell culture experiments, aseptic operations should be strictly implemented to reduce various contaminations.
The FAI climbed 5.9 percent year-on-year in the first 11 months of 2018, quickening from the 5.7-percent growth in Jan-Oct, the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) said Friday in an online statement.
The key indicator of investment, dubbed a major growth driver, hit the bottom in August and has since started to rebound steadily.
In the face of emerging economic challenges home and abroad, China has stepped up efforts to stabilize investment, in particular rolling out measures to motivate private investors and channel funds into infrastructure.
Friday's data showed private investment, accounting for more than 60 percent of the total FAI, expanded by a brisk 8.7 percent.
NBS spokesperson Mao Shengyong said funds into weak economic links registered rapid increases as investment in environmental protection and agriculture jumped 42 percent and 12.5 percent respectively, much faster than the average.
In breakdown, investment in high-tech and equipment manufacturing remained vigorous with 16.1-percent and 11.6-percent increases respectively in the first 11 months. Infrastructure investment gained 3.7 percent, staying flat. Investment in property development rose 9.7 percent, also unchanged.
 English
English